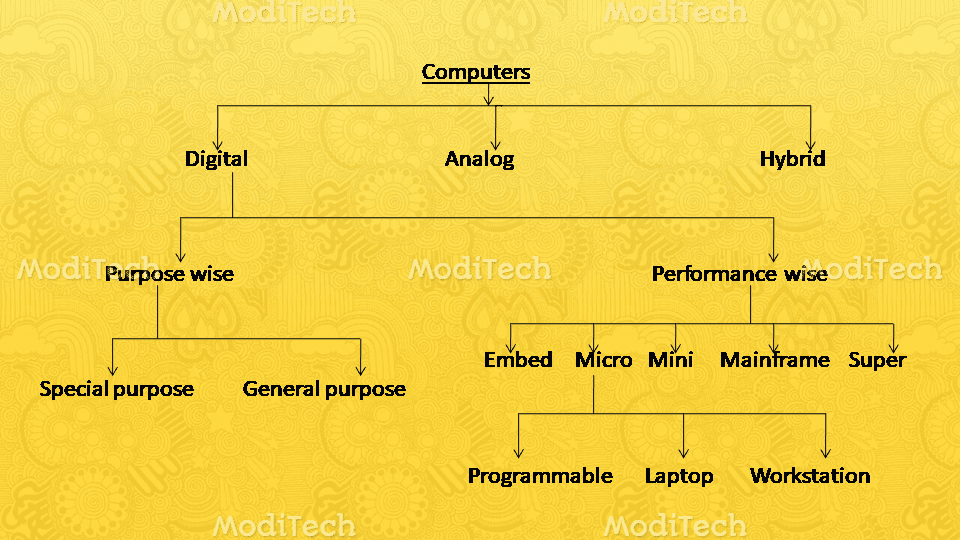
Types Of Computers
The computer has been classified into three categories these are given below:
1. Digital Computer
2. Analog Computer
3. Hybrid Computer
◈ Digital Computer
The Digital computer work on discontinuous data. they convert the data into digits and all operations are carried out on these digits at extremely fast rates.
Digital Computers are classified as:-
1. Purpose Wise
2. Size and Performance-Wise.
1. Purpose wise
:-Purpose wise digital computers are further classified into two categories special-purpose and general-purpose computers.
➺ Special purpose.
➺ General-purpose.
◊ Special Purpose Computer is designed to perform a specific task. The programs to carry out a task are permanently stored in the machine. For scientific tasks, this type of computer works efficiently but such computersare not versatile.
◊ General Purpose Computer is the one that can work on different types of programs and thus be used in many applications. The programs are not permanently stored but are input at the time of execution. These computers are very versatile.
2.Size and Performance wise
The Size and Performance-wise digital computers are further classified into five categories Micro, Mini, Mainframe, Embed, and super, etc.
➺ Micro Computer
➺ Mini Computer
➺ Mainframe Computer
➺ Embedded Computer
➺ Super Computer
◊ Micro Computer
A microcomputer is a computer whose CPU is a microprocessor. It is the smallest category of a computer having a microprocessor as its CPU. A microprocessor is a processor whose all main components are on a single integrated circuit chip. Those are normally single processor, single-user systems designed for performing basic operations like educational, small business applications, playing games, etc. IBM PCs, Apple Mac, IBM PS/2 are some popular microcomputers.
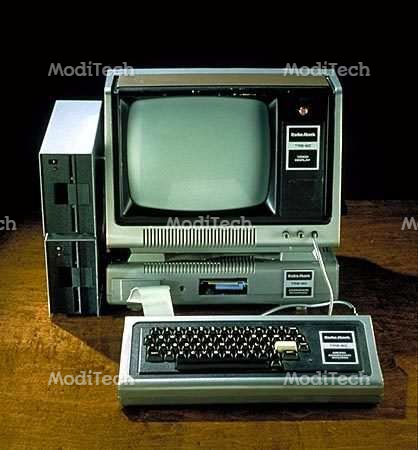

◊ Mini Computer
Minicomputers are more powerful computers than microcomputers in terms of processing power and capabilities. They are a relatively fast but small and inexpensive computer with somewhat limited input/output capabilities. They are mainly multiuser systems and possess greater storage capacity and larger memories as compared to microcomputers. Examples for minicomputers are PDP-11, VAX 7500, MAGNUM, etc.

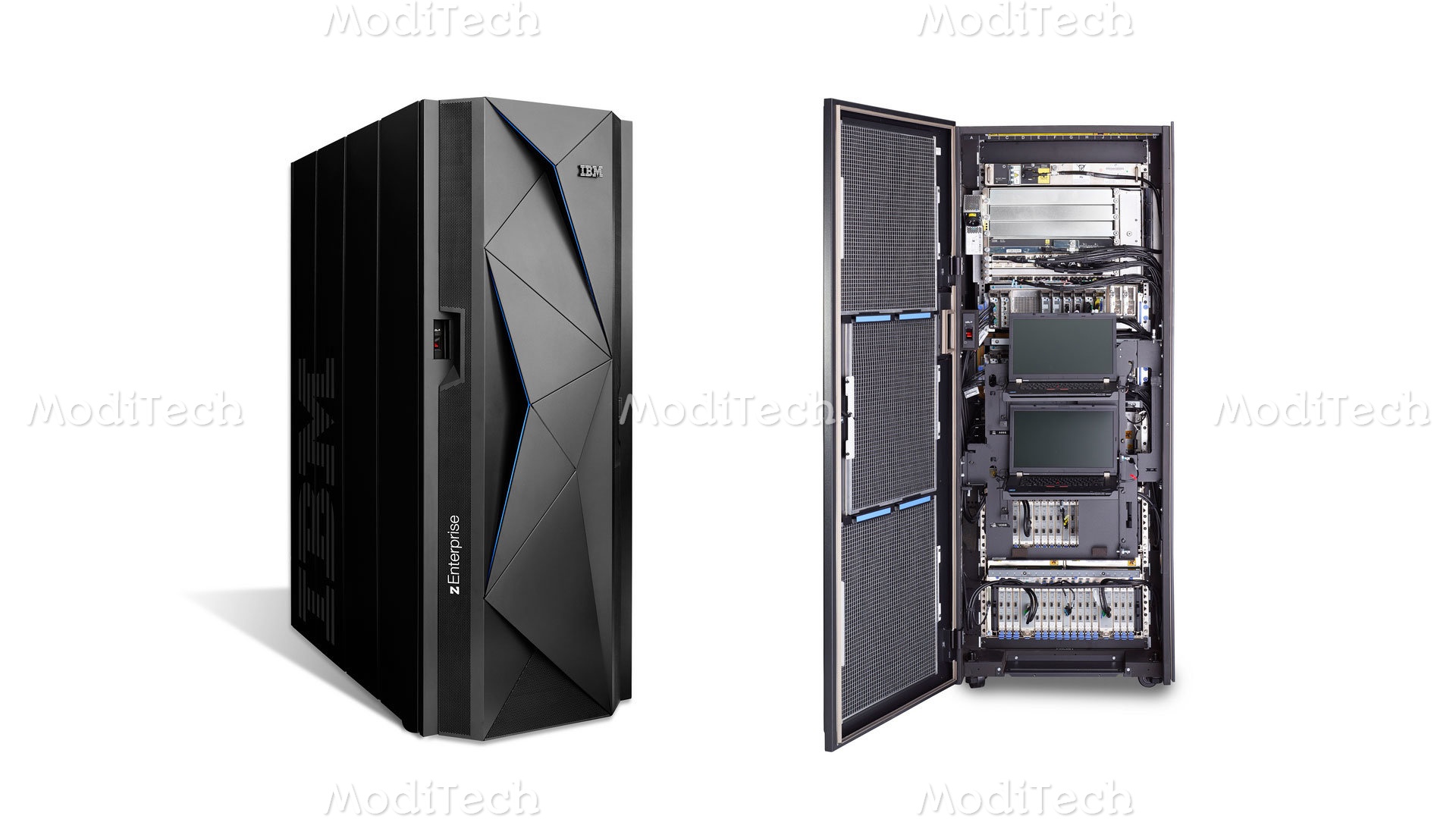
◊ Mainframe Computer
Mainframe computers are designed to handle huge volumes of data and information. They can support more than a hundred users at the same time and are very large and expensive computers having great processing speeds and very large storage capacity as compared to minicomputers. They even possess and work with more than one processor at the same time. So they are multiuser, multiprocessor systems. Very sophisticated operating systems are needed to control and supervise the operation of these mainframecomputers. Examples of mainframe computers are ICL 39, CDE 6600, VAX 8842, IBM 3090/600, IBM 4381.

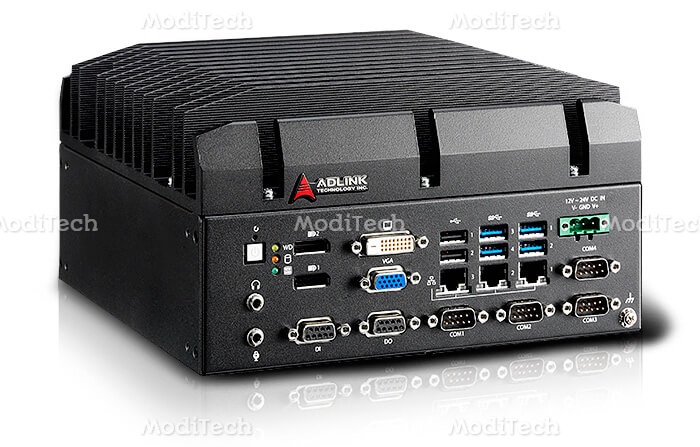
◊ Embedded Computer
Embedded Computer System is a combination of hardware and software, that is used to perform a specific task only. It may or not be programmable, depending on the application. Examples of embedded systems include washing machines, printers, automobiles, cameras, industrial machines, and more.

◊ Super Computer
Supercomputers are the most powerful computers among digital computers. They consist of several processors running together so that they are capable of handling huge amounts of calculations at higher speeds that are beyond human capabilities. Supercomputers can perform billions of instructions per second. Some of today's supercomputers have computing capability equal to that of 40,000 microcomputers. These are mainly used in applications like weather forecasting, nuclear science research, aerodynamic modeling, seismology, metrology, etc. Examples of supercomputers are CRAY X-MP/14, CDC - 205, ETA GF-10, FUJITSU VP-400, NEC SX-2, PARAM, ANURAG. PARAM and ANURAG are supercomputers produced by India.

◈ Analog Computers
In anAnalog computer, continuous quantities are used. Computations are carried out with physical quantities such as voltage, length, current, temperature, etc. Readings on a dial or graphs are obtained as the output, ex. Voltage, temperature; pressure can be measured in this way.


◈ Hybrid Computers
:-Hybrid computers utilize the best qualities of both the Digital and Analog computer. In these computers, some calculations take place in an analog manner, and the rest of them digitally take place.


You might like this :-
○ Generation of computer
○What is software?
○Architecture of Computer
○Operating System