Architecture of CPU (Processor)
♢ Processor (CPU)
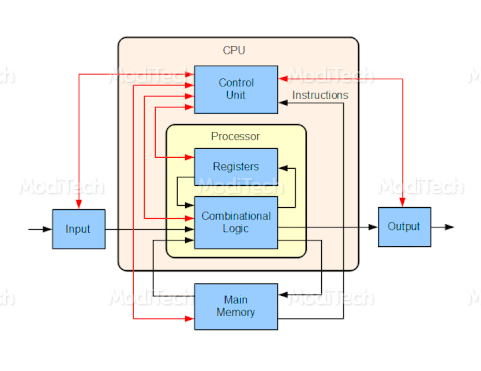
The Central Processing Unit (CPU) is also known as PROCESSOR or MAIN PROCESSOR. It is an integrated circuit which operates all the operation of the computer. It accepts data, performs operations on the data, and sends output results to thecomputer. Information from an input device is communicated via the bus to the Central Processing Unit (CPU), which is the part of the computer that translates commands and runs programs. It consists of ALU and CU, and a single chip or series of chips that perform arithmetic and logical calculations and controls the operations of the other elements of the system
♢ Arithmetic Logical Unit (ALU)
It is a digital integrated circuit in the processor which carried out arithmetic and logical operation on integer binary number. The data is stored in the primary storage unit and transferred to the ALU whenever needed. Data can be moved from the primary storage to the arithmetic logic unit. After the completion, the results are sent to the output storage section and the output devices. It is the opposite of a floating-point unit that operates on floating-point numbers.
♢ Control Unit (CU)
CU stands for Control Unit. It is part of a processor (CPU) that tells the processor how to execute the operation. It controls all other components of the CPU such as ALU, Memory, Input, and Output Devices. It manages all the resources of the computer. It controls entire parts of the computer and it gets the instructions from the programs stored in the primary storage unit interprets this instruction and subsequently directs the other units to execute the instructions. Thus it manages and coordinates the entire computer system.
♢ Main Memory
Main memory is also known as Primary memory. The primary is the central storage of computer system which based on the semiconductor memory circuit. It is part of the main computer system. All the information CPU use, that is stored and accessible from the primarymemory. It lost the data when the power supply(electricity) is off.
♢ Combinational Logic
Combinational Logic is also known as Time-Independent Logic. It is used to perform boolean operations and it is the opposite of sequential logic. It is a connected arrangement of logic gates with a set of input and output. It is a combination of all logical units such as FPU and ALU.
♢ Input Device
An Input Device refers to any hardware components used to enter data, program, commands, and user response into the computer. It is known as an Input Device. For example:- Keyboard, Mouse, Scanner, Joystick, OCR, Lightpen, Microphone, etc.
♢ Output Device
Once data has been input into the computer and processed, It is of little use unless it can be retrieved quickly and easily from the system. the computer must be connected to an output device. Theoutputunits accept the results produced by the computer, convert them into a human-readable form and supply them to the users.
♢ Floating Point Unit (FPU)
The Floating Point Unit is also known as a math coprocessor or numeric coprocessor that is integrated into the processor. It is a specialized coprocessor that operates on numbers faster than the microprocessor. It is used to operate on floating-point numbers such as Addition, Subtraction, multiplication, division, Square Root, etc. Some FPU has also performed operations like exponential or trigonometric calculation.
♢ Coprocessor
Coprocessor is an additional processing unit to improve the functionality of the CPU. It is parts of the processor that integrated within the processor. It is used to speed up the performance of the CPU. It manipulates numbers more quickly than the basic microprocessor circuit does. It offloads other processor-specific tasks from the main processor (CPU) and speeds up system performance.
♢ L1 and L2 Cache memory
L1 and L2 cache memory are levels of cache memory. The processor process any data and it need for next task, the cache memory store the processes data and it saves time in compared to get data from RAM. Level 1 cache memory is faster accessible than Level 2 cache memory. If the data didn't find in L1 cache memory then it will access L2 cache memory. L1 comes with a memory size of 32000bytes and whereas L2 comes with 1024 kilobytes.
♢ Registers
A register is accessible by the processor for faster processing of data. It holds instruction and other data that are frequently used by the CPU. It supplies operands to ALU and stores the results of operations. The main purpose of using a register is to retrieve data quickly forprocessingother data. It generally comes in the size of 8 bit, 32 bit, 64bit register.
♢ Microprocessor
The microprocessor consists of the Arithmetic Logical Unit (ALU), Control Unit (CU), and special-purpose storage areas called registers. Using ALU, a microprocessor can perform an arithmetic operation such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. Modern microprocessors contain floating-point units that can perform any complex operation on large floating-point numbers. During its ALU operation, the microprocessor holds its intermediate results in special-purpose registers. These registers are not accessible to the user.
♢ Internal Bus
Network of communication lines that connects the internal elements of the processor and also leads to external connectors that links the processor to the other elements of thecomputer
Components of CPU (Processor)
♢ The System Unit (CPU Cabinet)
A system unit is a box-like unit filled with several useful components, each performing a discrete function. These components work together to accomplish the main function of the computer, viz. accept and process input and deliver output. This section will elaborate on these components one by one.
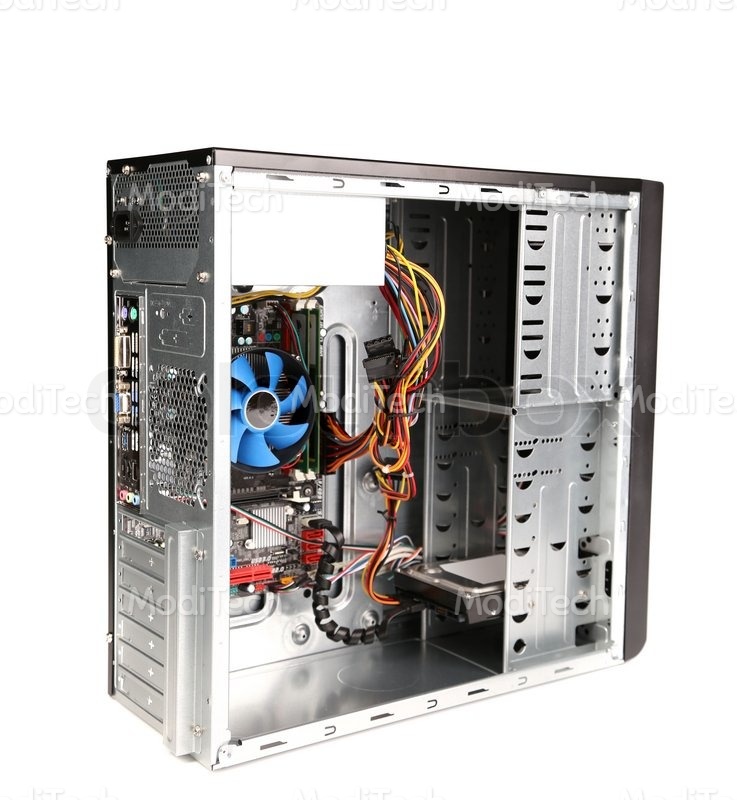

♢ Internal Power Supply
The system unit draws power from the AC mains through a power protection device. This power is not directly supplied to the internal components. Instead, one of the components, called the internal power supply, converts the AC input into DC output of 5 and 12 volts. Normally, the internal power supply is referred to as Switched Mode Power Supply (SMPS). The SMPS provides cable connectors to supply the required voltage to the other internalcomponentslike the floppy drives, the hard disk drive, the motherboard, and external devices such as the keyboard. The ON/OFF switch of the system unit is a part of the SMPS. Thus, when you switch the system unit on or off, you switch the SMPS on or off shows the various components of the system unit.

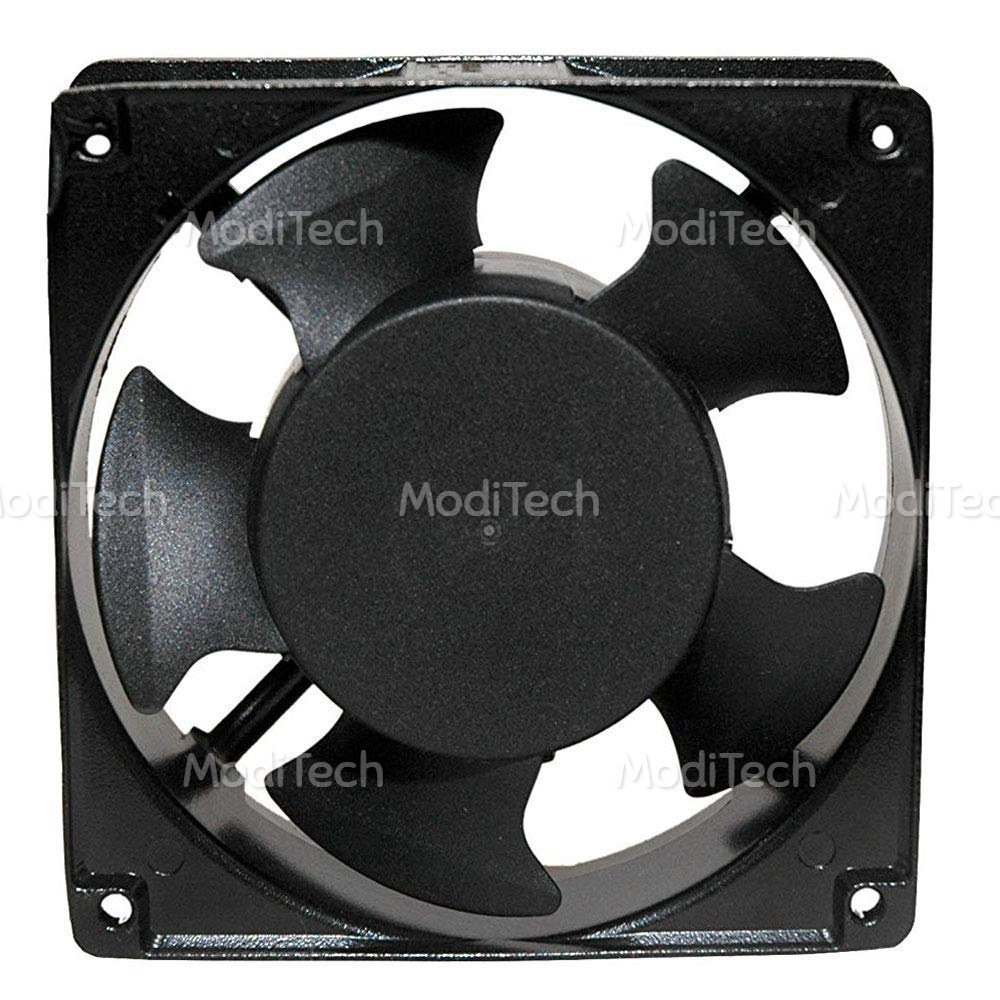
♢ Exhaust Fan
The SMPS has a small fan, called the exhaust fan, attached to it. This fan rotates as long as the computer is switched on Its function is to cool the SMPS unit.

♢ Speaker
The system unit also has a small audio speaker attached to it. This speaker is connected to the motherboard and produces a sound whenever instructed by software programs. For example, when the machine starts a self-test program is executed that uses a beep to indicate that everything is working satisfactorily. It is also used by entertainment programs to produce sound effects.

♢ Motherboard
When you open the system unit, a large board containing several tiny electronic circuits and other components is visible. This is called the motherboard. All peripheral devices are connected to themotherboard. In an IBM PC, the motherboard is called the system board.

You might like this :-
○ Generation of computer
○Types of computer
○Architecture of Computer
○Output device